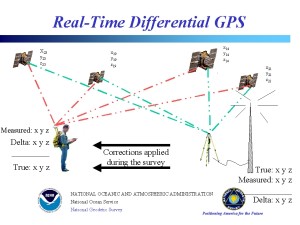
Differential Global Positioning System
DGPS (Differential Global Positioning System) is a complementary positioning system, which improves the accuracy of GPS. It uses a reference receiver whose position is known, and a second receiver. With the reference receiver, the differences between the known position and the GPS-calculated position are calculated, after which the deviations are sent to the receiver. The calculated positions of the receiver are then corrected, resulting in an accuracy of approximately 2 meters in x and y. The receiver is then used to calculate the difference between the known position and the GPS-calculated position.
This may be too inaccurate for fieldwork. On the other side of the scale there are rtk-DGPS’s, which, with the help of a fixed station, can work to the nearest centimetre.
Reference receivers are placed all over the world and transmit a modulated correction signal to the 283.5 to 325 kHz band over the radio beacons of sea and coastal shipping. The correction signals can be identified by a unique identification number that is sent with the corrections. The International Association of Lighthouse Authorities (IALA) is the organisation that takes care of the worldwide chain of MF radio beacons.